Chapter 12: Oral Reports
Katrina Peterson
Chapter Synopsis
This chapter shares basic principles for the preparation and delivery of oral reports. It gives an overview of expected structural conventions: how to set up an introduction, body, and conclusion. Since presentations often include a visual component, the chapter offers guidelines for creating an effective PowerPoint, Prezi, or Keynote. It includes tips for developing effective slides, while acknowledging the drawbacks of presentation software. It also offers suggestions to help speakers prepare well, overcome anxiety, and consider their speaking context. The chapter concludes with thoughts on presentation delivery.
12.1 Introduction to Oral Presentations
Increasingly, employers report that they require excellent communication skills, not just in print but also in person. Your employer will likely call on you to deliver an oral report at some point in your career. Whether you are an engineer or a writer, a professional or a student, a business person or a scientist, you will need to communicate well with supervisors, colleagues, clients, and the public. For most, this includes at least an occasional formal presentation. Formal presentations in the workplace usually take one of three forms: 1) informational, 2) persuasive, or 3) instructional. Informational presentations are useful for reporting on research or giving a project update. Persuasive presentations can be used to make pitches to clients or supervisors. Instructional or how-to presentations are formatted to teach, explain, or train. In each instance, you will have a chance to showcase your skills, often hybridizing or combining different modes of communication based on your past training. For example, a how-to presentation would connect your ability to write clear technical instructions with your ability to present well. Your goal as a speaker will differ based on context, but the best presentations share certain characteristics that you will want to consider.
In technical presentations, like most other genres of technical communication, good visual information design is essential. (See Chapter 5 on document design for additional tips and guidelines.) Visual aids are useful for increasing audience understanding of both the subject and the organization of a presentation. Presenters should remember they have an array of options for visuals, from live demonstrations and interactive activities to old fashioned white boards; however, presentation software is the most commonly used option. Of the presentation software choices, PowerPoint is widely used in the workplace and in educational settings. Other software like Prezi or Google Slides are becoming more popular and present may of the same opportunities and challenges. As you think through your options, be aware that each choice has its strengths and weaknesses. For example, PowerPoint can be a very effective tool for students and professionals if used appropriately, but effective use of this tool is not as intuitive as one would think. The following sections will help you to structure your presentation well and to consider the pros and cons of each design choice.
12.2 Presentation Structure
A clear presentation structure is an essential aspect of speech preparation. Similar to the academic essay and other genres of writing, a speech has three parts: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Each of these three parts includes certain patterns or rhetorical moves that the speaker should incorporate.
When structuring your presentation, it may be helpful to first draft an outline. This method enables you to determine essential content and main points, while excluding information that is not strictly relevant to your big-picture goals. You have different options to ensure that all the essentials are included; for example, you can place your major points on slides and then illustrate with examples you have prepared. Other options include carrying notecards or an outline to the podium, depending on the setup.
As you make these decisions, always consider who you are as a speaker, or your unique speaking style and challenges. If your hands tend to shake a bit, it may be helpful to hold something to steady them, but if you are concerned about the possibility of holding multiple materials (and possibly dropping them), you can confine memory aids to a single sheet of paper. It may be wise to carry a brief outline of major points with you to offset the possibility of omitting important information. This strategy also helps to avoid losing main points in the case of a technology malfunction if you will be referencing slides.
Introduction
Introductions and conclusions are points of emphasis; psychologically speaking, we tend to remember information presented first and last more clearly than information that is buried in the middle. The first words you say will also set the tone for the rest of your speech. There may not be any one best way to start a speech, but the following are some helpful guidelines that will make starting a speech much easier.
Perhaps most importantly, capture the audience’s attention as you introduce the topic. If you do not engage the audience at the outset, it will become more difficult to do so as you continue speaking. Starting a speech with “Hey everybody. I’m going to talk to you today about soccer” already sounds boring and will not engage audience members who are not soccer fans. If your audience has deemed your speech to be boring, trying to inform, persuade, or entertain them becomes exponentially more difficult. Instead, consider utilizing some of the techniques suggested below.
When selecting an opener, you want to make sure that the option you choose is appropriate and relevant to your specific audience. Different audiences will have different backgrounds and knowledge, so you should first determine whether specific information you plan on using would be appropriate for them. For example, if you are giving a speech on family units to a group of individuals over the age of 65, starting your speech with a reference to the television show Gossip Girl may not be the best idea because the audience may be unfamiliar with that show. Also choose an attention-getting device appropriate for your speech topic. Ideally, your attention-getting device should have a relevant connection to your speech.
For easy reference, here are some common devices used as speech openers:
- An anecdote or reference to current events engages an audience with a brief account or story. Notice the emphasis here is on the word “brief.” A common mistake speakers make when telling an anecdote is to make it too long. The anecdote should be short and have a clear point. For example, consider this attention getter for a persuasive speech on frivolous lawsuits: “On January 10 of this year, Scott Anthony Gomez, Jr., and a fellow inmate escaped from a Pueblo, Colorado, jail. During their escape the duo attempted to rappel from the roof of the jail using a makeshift ladder of bed sheets. During Gomez’s attempt to scale the building, he slipped, fell forty feet, and injured his back. Gomez then filed a lawsuit against the jail for making it too easy for him to attempt an escape.” In this case, the speaker is highlighting a news event that illustrates what a frivolous lawsuit is, setting up the speech topic about a need for change in how such lawsuits are handled. Your speech topic is the purpose of the attention getter, not the other way around, so be sure to avoid any material that seems overly personal or does not fit the subject.
- A startling statement/statistic/fact can engage your audience with relevant information about your topic. If your speech is about oil conservation, you could start by saying, “A Boeing 747 airliner holds 57,285 gallons of fuel.” A speech on the psychology of dreams might begin with this thought: “The average person has over 1,460 dreams a year.” Although startling statements are fun, it is important to use them ethically. (See Chapter 4 on ethics for more information on ethics and professional communication.) Make sure that your opening statement is factual. The internet is full of startling claims that are simply not accurate, so when you find a statement you would like to use, you have an ethical duty to ascertain its truth (and cite it correctly) before you use it.
- A rhetorical question may be a good way to draw your audience into your topic. For example, a speaker talking about the history of Mother’s Day could start by asking the audience, “Do you remember the last time you told your mom you loved her?” In this case, the speaker does not expect the audience to shout out an answer, but rather to think about the question as the speech continues.
- A direct reference to your audience may be an excellent method to engage them. Your audience is the single most important factor is crafting your speech, so it makes sense that you might acknowledge them in some way. Here is an example: “As students at Oklahoma State, you and I know the importance of selecting a major. In today’s competitive world, we need to choose a major that will lead to employment and provide us with fulfilling careers. That’s why I want you all to consider majoring in communication.” In this example, the speaker reminds the audience of their shared status as Oklahoma State students and uses this common ground to acknowledge the importance of selecting a major.
- An opening quotation is another way to capture your listeners’ attention. Maybe you will find an interesting quotation in one of the articles or books you read while researching your speech. Quotations may add an element of fun to a speech: “As the late actress, fashion icon, and social activist Audrey Hepburn once noted, ‘Nothing is impossible. The word itself says I’m possible’!” As with this example, be sure to credit the source first if you use a quotation as your attention getter.
- Humor can be a great way to engage an audience, but it is a double-edged sword. If you do not wield the sword carefully, you can lose your audience very quickly. One of the biggest mistakes a speaker can make is to use some form of humor that the audience either does not find funny or, worse, finds offensive. Think about how incompetent the character of Michael Scott seems on the television program The Office, in part because of his ineffective use of humor. As with other attention-getting devices, your humor must be relevant to your topic and must respect your audience’s sensitivities.
This list of opening devices represents a starting point for beginning your speech. As indicated, your selection of attention getter is not only dependent on your audience, your topic, and the occasion, but also on your preferences and skills as a speaker.
Body
As with the other sections of the presentation, keep in mind the importance of audience engagement. In general, the more interactive the presentation, the better; the more you know your audience, the better. Remember that each person’s learning style differs from the next, so do your best to engage your audience in different ways, possibly by including details that appeal to the five senses (sensory details). You might also include audio, tactile, and/or kinesthetic components in addition to your chosen visual.
With experience, you will learn to gauge your audience’s level of engagement and make small adjustments that help them to stay involved. Depending on context, it may be appropriate to include some movement; perhaps you ask your audience to engage with one another in small groups, which causes a small spatial shift, or perhaps you yourself take a few steps closer to a whiteboard. Integrating props or relevant hand gestures may achieve a similar effect. Our eyes naturally follow movement, so something as simple as walking across the room can serve to include more members of the audience and help them to re-engage. The techniques you can employ within the body of a presentation are many and various, but as above all, know yourself and know your audience. (See Chapter 2 for additional information on audience.)
Conclusion
The conclusion has three specific elements that you will want to incorporate. Given the nature of these elements and what they do, these should generally be incorporated into your conclusion in the order they are presented below.
- Signal the end. A good conclusion should clearly signal the end of a speech. You may be thinking that telling an audience you are about to end is a no brainer, but many speakers do not prepare their audience for their conclusion. When a speaker just suddenly stops speaking, the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead, give listeners a clear signal so that they can mentally organize and catalog all the points you have made for further consideration later.
Generally, the easiest way to forecast the end of your speech is to include a verbal signal that is meta-discursive (or self-referential in some sense, referring back to the speech itself). Within a public speaking context, periodic meta-discursive references help an audience to track a speaker’s progress from introduction to conclusion. Common formulations include phrasings like in conclusion, in summary, and to conclude. Depending on your audience, you may choose a more conversational or creative method of signaling; you will want to make sure that the framing does not sound too cliché. You have many options, but it should be clear to everyone that you are about to conclude. Also be aware that some of the common formulations (and saying them more than once) can have an unintended negative effect. The audience may decide you are finished and tune out, like how movie-goers get up and leave during the credits in a movie. If this is a concern, you can instead go straight to the summary explained further below.
- Restate main points. In the introduction of a speech you delivered a preview of your main points; in the conclusion you will likely deliver a review. Repetition is especially important in oral communication; include planned redundancy, but avoid being overly redundant. Just as you discussed and made transitions to your main points during the body of the speech, be sure to review the main points in the conclusion. These steps increase the likelihood that the audience will retain your main points after the speech is over.
As you review, avoid introducing new material or ideas. For example, if you said, “There are several other issues related to this topic, such as…but I don’t have time for them,” the audience may wonder why you did not address those in the body section. If you were giving a persuasive speech on wind energy and ended with “wind energy is the energy of the future, but there are still a few problems with it, such as noise and killing lots of birds,” you are bringing up a counter-argument that should have been dealt with in the body of the speech. The conclusion is not the place for new material.
- Include a clincher. The third element of your conclusion is the clincher, a memorable ending sometimes referred to as a concluding device. Make these words count, since they are the last you will include in the speech. In a sense, you could think of your speech as a nice dinner at a fancy restaurant: the introduction is the appetizer that gets everyone ready for the main course, the body section is the “meat and vegetables,” and the conclusion is like dessert. But have you ever had a nice meal that ended with an unappetizing dessert? Regardless of how good the rest of the meal was, you probably walked away with a negative final impression.
The clincher is like the inverse of the attention-getter. You want to start the speech strong, and you want to end the speech strong. There are a number of ways you can make your clincher strong and memorable. You can conclude with a challenge, or a call to action. In a speech on the necessity of fund-raising, a speaker could challenge the audience to raise 10% more than their original projections. In a speech on eating more vegetables, a speaker could challenge the audience to increase their current intake of vegetables by two portions daily, asking audience members to take a specific action or make a change. Challenges can be aspirational and they can be inspirational, but they should always be reasonable; the audience should see the challenge as attainable.
12.3 Presentation Options
Quite often, you will have to prepare visual materials to accompany your talk. You might prepare handouts, but it is even more probable that you will need to prepare materials that can be projected on a video screen. The classic version of these projected materials is the overhead transparency, a thin sheet of clear plastic that you can run through a laser printer or write on with special markers; this medium is quickly disappearing, although it still surfaces. Sometimes, you might be able to project paper documents to a screen via a document camera, but doc cams are becoming less common, and they can only present static images.
Instead, you will most likely be asked to create a dynamic presentation using software such as PowerPoint, Prezi, or Keynote. Many other programs exist, including what Google has to offer, but these are among the three most common presentation programs. Each program has its own special abilities and strengths; however, they all share common basic principles that you can use to create memorable, effective, and interesting presentations. The following information will help you with selecting an effective presentation format.
Three Major Presentation Formats
For a presentation using PowerPoint, Prezi, or Keynote, you can choose from three general formatting options: 1) bullet points, 2) illustrated points, and 3) speaker’s prop. The format you choose should fit your audience and your presentation’s subject.
Bullet Points. The bullet points format is the default layout for most PowerPoint users and viewers. Slides created in this format commonly include a title across the top and a cascading series of bulleted lines of text inside a slide’s main text box. Here is an example of this kind of slide:

Bullet points format presentations have several benefits. First, they are easy to prepare. (Just type, press Enter for a new line, and hit Tab to create a smaller bullet or Shift+Tab to make a larger bullet.) Secondly, they are useful for highlighting important words or naming concepts that an audience needs to learn. Finally, they project a serious tone and sense of professionalism.
As you consider these options, keep in mind that bullet points format presentations may be boring unless precautions are taken to keep the audience engaged; an overload of words may also make your audience cringe or lose interest. You have probably endured at least one bad PowerPoint in your life, and odds are, that bad presentation used the bullet points format.
Illustrated Points. The illustrated points format is similar, but slides created in this type of presentation focus on pictures, and text appears in a supporting role. An example of this kind of slide appears below.
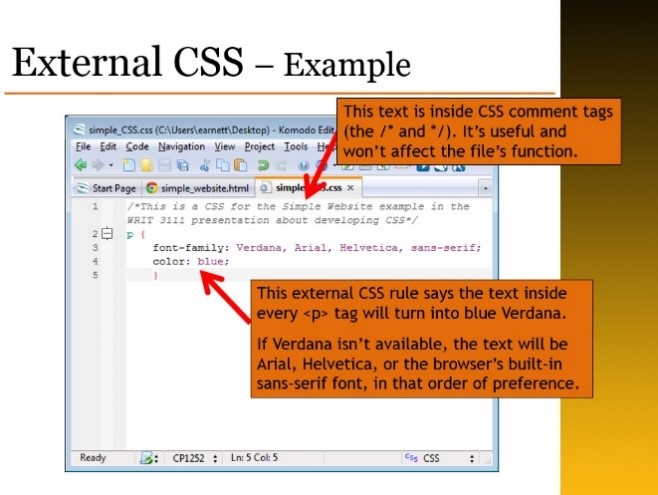
Illustrated points format slides have several benefits. They are excellent for showing conceptual relationships or demonstrating physical relationships between objects. People often respond positively to pictures, so illustrated points format slides also tend to capture viewers’ interest more than all-text presentations do. These slides require more detailed preparation, however, and they tend to be more visually busy. If your audience has problems concentrating, if you need to highlight important words, or if you need to move quickly through the information on the slides, you may want a more text-based approach. Illustrated points format slides can also be combined with bullet points format slides inside the same presentation.
Speaker’s Prop. The speaker’s prop format is similar to the illustrated points format, but a speaker’s prop almost entirely consists of simple pictures that flash onscreen in rapid sequence. Any text that appears is very short, uses a large font, and only appears for a moment. A speaker’s prop is appropriate for abstract subjects (e.g., the nature of free will), and if it is done well, it can be fascinating and will engage an audience. However, this type of presentation is often more complex and time-consuming to prepare than a presentation in the other formats, and you run the risk of making it so entertaining that the audience may remember the presentation but forget what you said. An example of a speaker’s prop presentation appears in the YouTube video below:
(https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=RrpajcAgR1E).
Whichever format you choose, remember that the presentation software is your servant; do not let it tell you what to do, and always modify a template to suit your needs. As an excellent example of what not to do, consider Peter Norvig’s classic Gettysburg PowerPoint: (https://norvig.com/Gettysburg/).
It serves as a satirical example of how an excellent speech—in this case, Abraham Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg Address, widely considered one of the classic speeches in the English language—can be ruined by using presentation software default settings and following a built-in template without modifying it.
12.4 Slide Design Tips
The guidelines in the design chapter—CRAP in particular—will help you create consistent, helpful, and visually appealing slides. But all the design skill in the world will not help you if your content is not tightly focused, smoothly delivered, and visible. Slides overloaded with text and/or images will strain your audience’s capacity to identify important information. Complex, distracting transitions or confusing (or boring) graphics that are not consistent with your content are worse than no graphics at all. Here are some general tips:
- Think simplicity. Use a small number of high-quality graphics and limit bullet points and text. Also avoid thinking of a slide as a page that your audience should read; instead, elaborate on major points with examples to keep the presentation interesting and pare down text as much as possible. Remember: even if you are presenting a slideshow, you want the audience to pay more attention to your words than to the slides themselves. Too much text will make the audience concentrate on reading slides instead of listening carefully to the verbal information.
- Break up your information. Organize the information into small chunks of text—phrases rather than complete sentences—to make sure your presentation flows well. Some experts recommend having no more than five bullet points per slide. If you do have more than five, you may want to set up the bullet points to appear a few at a time (in order, on separate slides, or in different columns) to avoid the distraction of a longer list.
- Have a consistent visual theme. Some pros advise that you avoid using the stock PowerPoint templates, but the Repetition and Alignment aspects of CRAP are so important that the templates may be your best starting point.
- Choose a simple color scheme. In general, three to six colors should provide variety without overloading readers. Be consistent in how you use the colors. For example, if you use red font for the first 12 slides, you should probably not switch to blue font in the last 12 slides unless there is a clear and logical reason for doing so.
- Choose your font carefully. Make sure the text is readable from a distance in a darkened room. Many guidelines suggest that you use at least a 24-point font. Contrast is also important; place dark font on a light background or vice-versa.
- Practice your presentation. Software is only a tool, and the slide projector is not presenting—you are in charge. Realizing this is half the battle.
- Use graphics. In general, substantive slides should present a graphic that illustrates or supports your main point. Instead of the typical topic and bullet point slide layout, a more effective strategy for PowerPoint presentations slides may involve offering a claim backed by visual support in the form of a photo, graph, illustration, chart, etc.
- Be careful not to overload the slide (with either too much text or too many graphics). There is not necessarily one rule of thumb for how much is too much, but be deliberate with choices.
12.5 Pitfalls of Presentation Software
Since Microsoft introduced PowerPoint in 1990, the conference room has never been the same. Millions were amazed by the speed with which a marketing professional or an academic could put together a consistent, professional-looking slide presentation. And then . . .
At some point, somebody with critical thinking skills asked a great question: “Do we really need all these slide shows?” The stock images of arrows, business people in suits, stick figures scratching their heads, and the glowing, jewel-toned backgrounds eventually looked tired and failed to evoke the “wow” reaction presenters desired.
Microsoft is attempting to refresh the design options for PowerPoint, and there are dozens of good alternatives, some of them free (Keynote, Slide Bureau, Prezi, SlideRocket, Easel.ly, Emaze, Slidedog). But the fundamental problem remains—text-heavy, unfocused, long presentations are the problem, not the software. If you are sure that a visual presentation will provide something necessary to your audience, keep the number of slides and the amount of text on each slide to a bare minimum. Think of a slide presentation as a way of supporting or augmenting the content in your talk; the slides should not replace your content.
Above all, do not read the slides to your audience, which is considered one of the single most annoying things a presenter can do; it also makes the presenter seem unprepared. Excessively small text and complex visuals (including distracting animations) are also frequently cited as annoyances. Instead, make sure that viewers can read slides easily from the back of the room. Also try to design your slides so that they contain information that your viewers might want to write down. For example, good presentations often contain data points that speakers cannot just rattle off or quick summaries of key concepts that viewers will not be able to make up on the fly. If you cannot explain how the slides add value to your presentation, it might be best to avoid using them altogether.
To get a feel for what may annoy your audience, try Googling “annoying PowerPoint presentations.” Also consider designing your presentation to allow for audience participation instead of passive viewing of a slideshow—a good group activity or a two-way discussion is a far better way to keep an audience engaged than a stale, repetitive set of slides.
In summary, a tool is only as effective as the person using it. Presentation software like PowerPoint does not make students stupid and professors boring; rather, poor use of this tool makes for ineffective presentations and can lead to laziness in both the audience and the presenter. Many of the problems with presentations result from readily accessible tools being used by individuals untrained in rhetorical and visual design. Fortunately, students of technical communication can implement a change of strategy to make presentations more effective.
12.6 Presentation Preparation
Research shows that public speaking rates among people’s top fears; some surveys suggest that it ranks above fear of surgery, or even death. Why do so many people dislike public speaking? This is a complex question, and the answer is tied to factors both personal and psychological, ranging from past experience and training to culture and context. The term glossophobia combines the Greek words for “tongue” and “fear or dread” to reference a severe fear of public speaking. People who suffer from glossophobia tend to freeze in front audiences. This fear may surface in situations such as responding to a professor in class or having to interact with a stranger, not just giving formal speeches.
Here are some strategies to help overcome anxiety as you prepare for your presentation. In addition to planning the details of content and delivery, be sure to prepare physically. Adequate sleep and rest are crucial. You might be thinking such a thing is impossible in college or in a demanding full-time job, where sleep deprivation and late nights come with the territory. However, research shows the extreme effects a lifestyle of limited sleep can have, far beyond yawning or dozing off in class. Energy levels (and your ability to be alert during the speech) will be affected by lack of sleep.
As you prepare, you may want to eat something that is protein-based before speaking. In other words, cheese or peanut butter on whole grain toast, Greek yogurt, or eggs for breakfast would be preferable to more sugary options. Also wear clothes that are comfortable but meet the context’s formality requirements. Wear the same outfit when you rehearse the presentation so that you will feel comfortable walking and moving in that attire. Comfortable, professional shoes will give you a firm base for your posture. You might consider utilizing some stretching or relaxation techniques that will loosen your limbs or throat. Tightening and stretching your hands, arms, legs, and throat for a few seconds before speaking can help release some of the tension. Also, bring something to drink to prevent dry mouth, and take several deep breaths (to release stress and steady your voice) before climbing on stage. People tend to speak faster and at a higher pitch when they are nervous and giving a presentation. Make an effort to speak at a comfortable pace and avoid letting your voice rise too high. Do not apologize before you give your presentation; being nervous is normal, and although you may feel jittery, chances are your audience will not mind or will not even notice.
Contextual Preparation
The more you can know about the venue where you will be speaking, the better. Whenever possible, check out the space in advance. For example, if you were required to give a short talk for a job interview, you would want to know what the room will be like, if there is equipment for projection, how large the audience will be, and how seating will be arranged. Consider practicing your presentation in a room that is similar to the actual space where you will deliver it. The best advice for contextual preparation is to be on time, even early. If you have to rush in at the last minute, it will be difficult to stay calm and focused for the speech. If you are early, you may be able to make sure equipment is working, or even converse with the audience as they enter. Professional speakers often do this to relax themselves, build credibility, and gain knowledge to adapt their presentations to the audience. Being on time will help you create a good first impression and thus enhance your credibility before the actual speech.
Procrastination and Preparedness
Procrastination is the great enemy of preparedness. Fluid, articulate public speaking requires repeated practice before the actual delivery. The first time that you say the words should not be when you are in front of your audience. Practicing is the best way to feel confident and in control of the words you speak. As you practice, time yourself to be certain that your speech meets the time limit; speaking within the expected time is a cardinal rule of public speaking. Practice aloud, preferably with someone to listen, while using your visual aids. If you can record yourself in order to analyze gestures and delivery, you will be able to fine-tune and adjust elements of your speaking style. The most effective way to gain a reputation as someone who does not respect an audience (or someone who should not be allowed to run meetings) is to talk longer than the allotted time. Not only will practice help you to feel comfortable with presentation delivery, but it will also ensure that you do not upset your audience by running over the time limit.
Final Note: If you are an audience member, you can help speakers to feel more comfortable, at least a little bit. Be an engaged listener from beginning to end. You can imagine that a speaker is going to be more nervous if the audience looks bored from the start. A speaker with less anxiety will do a better job and be more interesting, so give the speaker your full attention, nod along to main points, ask questions where appropriate, and stay off your phone unless you are using it to take notes.
12.7 Delivery Tips
What follows are some general tips you should keep in mind, but they all essentially derive from one very straight-forward premise: practice your speech beforehand, at home or elsewhere, the way you will give it.
- Practice your speech aloud. This technique enables speakers to learn the words and be prepared, but it also lets them know of any potential problems. Sentences on paper do not always translate when spoken. Practicing out loud allows speakers to identify and fix issues with pronunciation and delivery before getting up in front of the audience.
- Avoid excessive body movements. This includes nervous or unnecessary hand motions, unnecessary tapping of feet or hands, etc. But also avoid standing stock still; some hand gestures can keep the audience engaged.
- Eliminate filler words such as “uh” and “um.” Recording yourself, or asking a friend to listen to your speech, can help you to identify this tendency. In some cases, it may be possible to integrate meaningful pauses in the place of filler words to reduce their frequency.
- Project your voice. Soft-spoken speakers may have to speak louder to ensure that everyone can hear, while avoiding the appearance of shouting or reaching an awkwardly squeaky pitch. If you will be using a microphone, practice in advance how you will hold it and the volume you will use.
- Articulate sentences clearly. Again, be aware of your own tendencies. If you tend to elide words, or if you have a regional accent that differs from your audience’s, you may need to slow down and practice enunciating in a way that sounds natural rather than forced.
- Add inflection and expression. Presenters who speak in a monotone will have difficulty keeping an audience engaged.
- Refuse to become flustered. In many cases, an apology is unnecessary and will only draw undue attention to minor oversights, whether perceived or actual. Instead, take a breath, re-focus, and move on with the speech.
- Make eye contact. If it feels awkward to maintain direct eye contact, look around the room at forehead level, or a point slightly above viewers’ heads, making sure to include the entire audience.
- Maintain an open body posture. Crossed arms, for example, can make a speaker seem closed off to the audience. In contrast, open hand gestures that are not excessive tend to communicate a corresponding openness to audience engagement and ideas.
There is no preset pattern for perfect delivery. However, with practice everyone can improve. For a few additional tips and suggestions, check out this amusing TedX talk on YouTube by Will Stephen:
(https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8S0FDjFBj8o).
As you practice your presentation skills, remember that each speaker is entirely unique, and we each embody different experiences and interests. This means that all speakers must find their own most effective style.
Attribution
Material in this chapter was adapted from the works listed below. The material was edited for tone, content, and localization.
Exploring Public Speaking, by Kris Barton and Barbara G. Tucker, licensed CC-BY-NC-SA.
Technical Writing, by Allison Gross, Annamarie Hamlin, Billy Merck, Chris Rubio, Jodi Naas, Megan Savage and Michele DiSilva, licensed CC-BY-NC-SA.
ENGL 145 Technical and Report Writing, by the Bay College Online Learning Department, licensed CC-BY.

