4 Chapter 4 Informal Fallacies
Some arguments are faulty, not necessarily because of the truth or falsity of the premises, but because they rely on psychological and emotional ploys. These are bad arguments because people shouldn’t accept your conclusion if you are using scare tactics or distracting and manipulating reasoning. Arguments that have this issue are called fallacies. There are a lot of fallacies, so, again, if you want to know more a web search will be useful. We are going to look at some of the most relevant fallacies for our day-to-day experiences.
Accident
Definition: Applying a general rule to a specific case whose circumstances “accidentally” make the rule inapplicable.
Example: Cutting people with knives is a crime. Surgeons cut people with knives. Therefore, surgeons are criminals.
The general rule about cutting people doesn’t apply to surgeons operating in a medical context.

Ad Hominem
Definition: This fallacy is also referred to attacking the person. We commit this fallacy when we dismiss someone’s argument or position by attacking them instead of refuting the premises or support for their argument.
Example: I am not going to listen to what Professor ‘X’ has to say about the history of religion. He told one of his previous classes he wasn’t religious.
The problem here is that the student is dismissing course material based on the professor’s religious views and not evaluating the course content on its own ground.
To avoid this fallacy, make sure that you target the argument or their claims and not the person making the argument in your rebuttal.
Here’s a video clip from The Simpsons that highlights the ad hominem fallacy:
Amphiboly
Definition: Amphiboly is a logical fallacy that occurs due to ambiguous or unclear grammar or punctuation that creates multiple possible interpretations. The ambiguities we covered in chapter 3 are relevant here.
Example: I saw a man on a hill with a telescope.
This sentence is ambiguous because it could mean:
- I used a telescope to see a man on a hill
- I saw a man who was on a hill and had a telescope
- I saw a man who was on a hill that had a telescope on it
Here’s another example of the fallacy of amphiboly:
Appeal to Emotion
Definition: Arguments should be based on reason and evidence, not emotional tactics. When we use an emotional tactic, we are essentially trying to manipulate someone into accepting our position by evoking pity or fear, when our positions should actually be backed by reasonable and justifiable evidence.
Example: Officer please don’t give me a speeding ticket. My girlfriend broke up with me last night, my alarm didn’t go off this morning, and I’m late for class.
While this is a really horrible start to one’s day, being broken up with and an alarm malfunctioning is not a justifiable reason for speeding.
Here’s an advertisement that highlights appeal to emotion, specifically pity:
Appeal to Ignorance
Definition: This fallacy occurs when our argument relies on lack of evidence when evidence is actually needed to support a position.
Example: No one has proven that sasquatch doesn’t exist; therefore it does exist.
Example: No one has proven God exists; therefore God doesn’t exist.
The key here is that lack of evidence against something cannot be an argument for something. Lack of evidence can only show that we are ignorant of the facts.
Here’s a video clip from SpongeBob, highlighting the appeal to ignorance fallacy:
Appeal to Nature
Definition: Arguing that something is good because it is “natural,” or bad because it is “unnatural.”
Example: Vaccines are unnatural, therefore they are bad for you.
This ignores the fact that many “natural” things, like diseases, can be harmful, and that medical interventions, while not “natural,” can be beneficial.
Here’s a video highlighting the fallacy of appeal to nature:
Appeal to the People (Bandwagon Argument)
Definition: Arguing that something is true because it is popular or widely believed.
Example: Everyone knows that aliens have visited Earth, so it must be true.
Popular belief doesn’t guarantee truth.
Here’s an advertisement from McDonald’s that shows the bandwagon fallacy:
McDonald’s: America’s Favorite
Appeal to Threat
Definition: Using a threat of force or negative consequences to try to win an argument. This fallacy is commonly known as a scare tactic.
Example: Professor, I’d like you to remember that my mother is a dean here at OSU. I’m sure that she will be very disappointed if I don’t receive an A in your class.
This is a scare tactic and is not a good way to make an argument. Scare tactics can come in the form of psychological or physical threats; both forms are to be avoided.
Here’s a video clip from SpongeBob highlighting the appeal to threat fallacy:
Begging the Question
Definition: An argument begs the question when the argument’s premises assume the conclusion, instead of providing support for the conclusion. One common form of begging the question is referred to as circular reasoning.
Example: Of course, everyone wants to see the new Marvel movie is because it is the most popular movie right now!
The conclusion here is that everyone wants to see the new Marvel movie, but the premise simply assumes that is the case by claiming it is the most popular movie. Remember the premise should give reasons for the conclusion, not merely assume it to be true.
Here’s a video clip from The Simpsons that highlights the begging the question fallacy:
Burden of Proof
Definition: Incorrectly placing the burden of proof on the side that is claiming a lack of evidence or impossibility.
Example: An employee claims harassment without proof and argues that the employer cannot prove that she was not harassed.
The burden of proof always lies with the person making the claim, not on those who are questioning it.
Here is a Ted-Ed video focusing on the burden of proof fallacy:
Can you outsmart the fallacy that started a witch hunt?
Equivocation
Definition: In the English language there are many words that have different meanings (e.g. bank, good, right, steal, etc.). When we use the same word but shift the meaning without explaining this move to your audience, we equivocate the word and this is a fallacy. So, if you must use the same word more than once and with more than one meaning you need to explain that you’re shifting the meaning you intend. Although, most of the time it is just easier to use a different word.
Example: Yes, philosophy helps people argue better, but should we really encourage people to argue? There is enough hostility in the world.
Here, argue is used in two different senses. The meaning of the first refers to the philosophical meaning of argument (i.e. premises and a conclusion), whereas the second sense is in line with the common use of argument (i.e. yelling between two or more people, etc.).
Here’s a video clip from The Simpsons that features the fallacy of equivocation:
False Cause
Definition: Assuming that because one event followed another, the first event caused the second.
Example: After I started wearing this lucky shirt, my team won every game. Therefore, the shirt is making them win.
Correlation doesn’t equal causation.
Here’s a video clip from Friends, highlighting the false cause fallacy:
False Dilemma
Definition: Presenting only two options when more possibilities exist. This fallacy is also referred to as a false dichotomy.
Example: You’re either with us or against us.
This ignores the possibility of neutrality or alternative viewpoints.
Here’s a video clip from an episode of The Simpsons highlighting the false dilemma. In the video this fallacy is referred to the “Either/Or fallacy.”
Faulty Analogy
Definition: We often make arguments based on analogy and these can be good arguments. But we often use faulty reasoning with analogies and this is what we want to learn how to avoid.
When evaluating an argument that is based on an analogy here are a few things to keep in mind: you want to look at the relevant similarities and the relevant differences between the things that are being compared. As a rule, if there are more differences than similarities the argument is likely weak.
Example: Alcohol is legal. Therefore, we should legalize marijuana too.
So, the first step here is to identify the two things being compared, which are alcohol and marijuana. Next, note relevant similarities and differences. These might include effects on health, community safety, economic factors, criminal justice factors, and the like.
This is probably not the best argument in support for marijuana legalization. One could just as easily conclude that since marijuana is illegal, alcohol should be too. In fact, one might find that alcohol is an often abused and highly problematic drug for many people, so it is too risky to legalize marijuana if it is like alcohol.
Here’s a video clip from The Simpsons highlighting the fallacy of false analogy (otherwise known as weak analogy):
Weak Analogy (False Comparison)
Hasty Generalization
Definition: We make and use generalizations on a regular basis and in all types of decisions. We rely on generalizations when trying to decide which schools to apply to, which phone is the best for us, which neighborhood we want to live in, what type of job we want, and so on. Generalizations can be strong and reliable, but they can also be fallacious. There are three main ways in which a generalization can commit a fallacy: your sample size is too small, your sample size is not representative of the group you are making a generalization about, or your data could be outdated.
Example: I had horrible customer service at the last Starbucks I was at. It is clear that Starbucks employees do not care about their customers. I will never visit another Starbucks again.
The problem with this generalization is that the claim made about all Starbucks is based on one experience. While it is tempting to not spend your money where people are rude to their customers, this is only one employee and presumably doesn’t reflect all employees or the company as a whole. So, to make this a stronger generalization we would want to have a larger sample size (multiple horrible experiences) to support the claim. Let’s look at a second hasty generalization:
Example: I had horrible customer service at the Starbucks on 81st street. It is clear that Starbucks employees do not care about their customers. I will never visit another Starbucks again.
The problem with this generalization mirrors the previous problem in that the claim is based on only one experience. But there’s an additional issue here as well, which is that the claim is based off an experience at one location. To make a claim about the whole company, our sample group needs to be larger than one and it needs to come from a variety of locations.
Here is a video example of a hasty generalization, which is taken from jury deliberation in the film 12 Angry Men (1957):
Inappropriate Appeal to Authority
Definition: We are going to use authority figures in our lives (e.g. doctors, lawyers, mechanics, financial advisors, etc.), but we need to make sure that the authority figure is a reliable one.
Factors to look for here might include reputation in the field, not holding widely controversial views, experience, education, and the like. So, if we take an authority figure’s word and they’re not legit, we’ve committed the fallacy of appeal to authority.
Example: I think I am going to take my investments to Voya. After all, Steven Adams advocates for Voya in an advertisement I recently saw.
If we look at the criteria for evaluating arguments that appeal to authority figures, it is easy to see that Adams is not an expert in the finance field. Thus, this is an inappropriate appeal to authority.
Here’s a video clip from The Simpsons that highlights the inappropriate appeal to authority fallacy. In this video the fallacy is referred to as Appeal to Doubtful Authority.
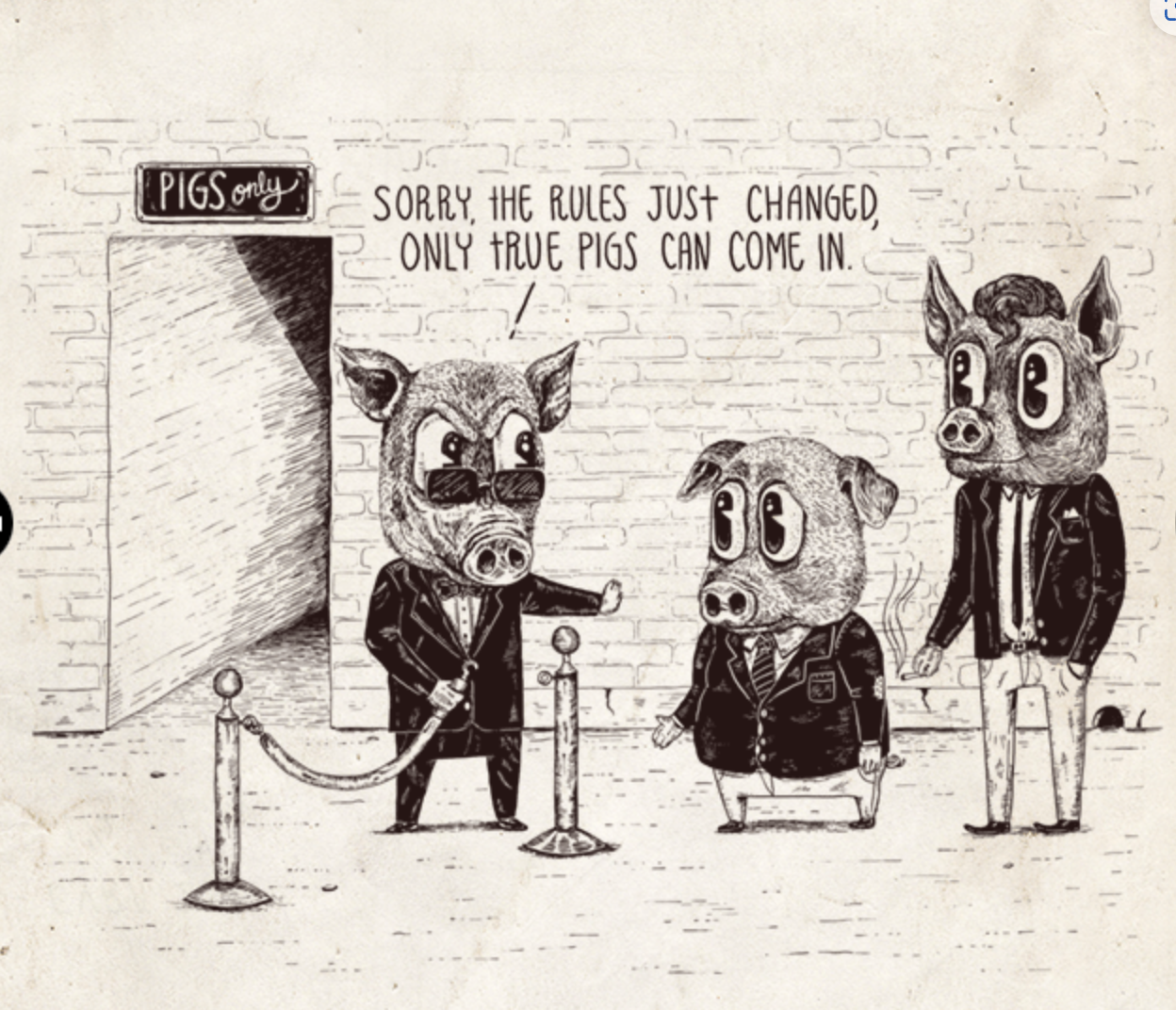
No True Scotsman
Definition: Changing the definition of a group to exclude a counterexample.
Example:
Person A: “No Scotsman puts sugar on his porridge.”
Person B: “But my uncle Angus is a Scotsman and he puts sugar on his porridge.”
Person A: “Ah, but no true Scotsman puts sugar on his porridge.”
The key is the arbitrary and post-hoc redefinition of the group to exclude the counterexample. This is what makes it a fallacy.
Here’s an image from An Illustrated Book of Bad Arguments, highlighting the no true Scotsman fallacy:
Red Herring
Definition: A red herring is a distraction or a change in subject matter. Sometimes this is subtle, but if you find yourself feeling lost in the argument, take a close look and make sure there is not an attempt to distract you.
Example: Can you believe that so many people are concerned with global warming? The real threat to our country is terrorism.
It could be the case that both global warming and terrorism are concerns for us. But the red herring fallacy is committed when someone tries to distract you from the argument at hand by bringing up another issue or side-stepping a question. Politicians are masters at this fallacy, by the way.
Here’s a video clip from Family Guy featuring the red herring fallacy:
Slippery Slope
Definition: Slippery slope arguments are found everywhere it seems. The essential characteristic of a slippery slope argument is that it uses problematic premises to argue that doing ‘x’ will ultimately lead to other actions that are extreme, unlikely, and disastrous. You can think of this type of argument as a faulty chain of events or domino effect type of argument.
Example: If you don’t study for your philosophy exam you will not do well on the exam. This will lead to you failing the class. The next thing you know you will have lost your scholarship, dropped out of school, and will be living on the streets without any chance of getting a job.
While you should certainly study for your philosophy exam, if you don’t it is unlikely that this will lead to your full economic demise.
One challenge to evaluating slippery slope arguments is that they are predictions, so we cannot be certain about what will or will not actually happen. But this chain of events type of argument should be assessed in terms of whether the outcome will likely follow if action ‘x” is pursued.
Here’s a video advertisement from DirectTV featuring the slippery slope fallacy:
Straw Man
Definition: A straw man argument is a specific type of argument that is intended to weaken an opponent’s position so that it is easier to refute. So, we create a weaker version of the original argument (i.e. a straw man argument), so when we present it everyone will agree with us and denounce the original position.
Example: Women are crazy arguing for equal treatment. No one wants women hanging around men’s locker rooms or saunas.
This is a misrepresentation of arguments for equal treatment. Women (and others arguing for equal treatment) are not trying to obtain equal access to men’s locker rooms or saunas.
The best way to avoid this fallacy is to make sure that you are not oversimplifying or misrepresenting others’ positions. Even if we don’t agree with a position, we want to make the strongest case against it and this can only be accomplished if we can refute the actual argument, not a weakened version of it. So, let’s all bring the strongest arguments we have to the table!
Here’s an image from An Illustrated Book of Bad Arguments, highlighting the straw man fallacy:

Conclusion
If you want extra practice with these fallacies, you can easily find examples online with an internet search. You can also view this book, An Illustrated Book of Bad Arguments, for free.
Informal Fallacies Quiz
Informal Fallacies Crossword
Chapter 4 Informal Fallacies, pt. I
Chapter 4 Informal Fallacies, pt. II
Chapter 4 Informal Fallacies, pt. III
Fallacy examples from the following sources:
Kim
Dowden
Cain
Van Cleave
Applying a general rule to a specific case whose circumstances "accidentally" make the rule inapplicable.
This fallacy is also referred to attacking the person. We commit this fallacy when we dismiss someone’s argument or position by attacking them instead of refuting the premises or support for their argument.
Amphiboly is a logical fallacy that occurs due to ambiguous or unclear grammar or punctuation that creates multiple possible interpretations.
Arguments should be based on reason and evidence, not emotional tactics. When we use an emotional tactic, we are essentially trying to manipulate someone into accepting our position by evoking pity or fear, when our positions should actually be backed by reasonable and justifiable evidence.
This fallacy occurs when our argument relies on lack of evidence when evidence is actually needed to support a position.
Arguing that something is good because it is "natural," or bad because it is "unnatural."
Arguing that something is true because it is popular or widely believed.
Using a threat of force or negative consequences to try to win an argument. This fallacy is commonly known as a scare tactic.
An argument begs the question when the argument’s premises assume the conclusion, instead of providing support for the conclusion.
Incorrectly placing the burden of proof on the side that is claiming a lack of evidence or impossibility.
In the English language there are many words that have different meanings (e.g. bank, good, right, steal, etc.). When we use the same word but shift the meaning without explaining this move to your audience, we equivocate the word and this is a fallacy. So, if you must use the same word more than once and with more than one meaning you need to explain that you’re shifting the meaning you intend. Although, most of the time it is just easier to use a different word.
Assuming that because one event followed another, the first event caused the second.
Presenting only two options when more possibilities exist. This fallacy is also referred to as a false dichotomy.
We often make arguments based on analogy and these can be good arguments.
If your sample size is too small, your sample size is not representative of the group you are making a generalization about, or your data could be outdated it is a variation of Hasty Generalization.
If we take an authority figure’s word and they’re not legit, we’ve committed the fallacy of appeal to authority.
Changing the definition of a group to exclude a counterexample.
A red herring is a distraction or a change in subject matter.
Slippery Slope fallacy uses problematic premises to argue that doing ‘x’ will ultimately lead to other actions that are extreme, unlikely, and disastrous. You can think of this type of argument as a faulty chain of events or domino effect type of argument.
A straw man argument is a specific type of argument that is intended to weaken an opponent’s position so that it is easier to refute.

