24 The Role of Information and Communication Technology in Natural Language Processing
Asabor Mary Bivwiere, Ph.D and Marshall Chime Opone
Abstract
This paper focuses on the role of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)in Natural Language Processing. The authors present ban introduction as well the motivation factors to their choice of the topic. In a step by step approach they discussed concisely the components of the concept of ICT, the Natural Language Processing (NLP) along side its frame work and some related concepts such as speech translation and problems associated with it. They equally cleared the coast of their major focus as they presented some devices useful in Natural Language Processing. Summary and conclusion of their discussion were equally presented.
Introduction
It is quite established that people convey their thoughts, ideas and experiences through very many ways, the best of which is through speech. For this reason, it is required that all necessary efforts should be made not to deprive those with problems in conceptualizing spoken words from the positioning of their lives. The problems with acquiring literacy skills are casually entailed by low-level auditory and/ or speech perception processes.
Numerous Nigerian children fall into the condition where English Language is used as the official language for delivering learning experiences. This, of a truth, has its negative effects. One of the negative effects is the creation of educational divides. To overcome these negative effects, the policy of the Universal Basic Education (UBE) which demands that Nigerian Local Language should be used in delivering learning experiences, particularly in the Nursery and Primary levels of education in Nigeria should be applauded. Adherence to this declaration will require that all teachers in these levels ought to speak and understand the pupils’ native language. This is a high mountain of task to achieve bearing in mind that Nigeria is a multi-lingual country. It is very difficult to find a teacher that can speak and understand two or more Nigerian native languages. It is against this backdrop that the need for a machine-based language translation system is required to provide the need of Nigerians: the natural language translation system, a subset of Natural Language Processing. Learners learn better when taught using their mother tongue. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESO) has encouraged mother tongue instruction in primary education since 1953 (UNESO, 1953; UNESO, 2008), and equally highlights the advantages of mother tongue education right from the start: children are more likely to enroll and succeed in school (Kosonen, 2005); parents are more likely to communicate with teachers and participate in their children’s learning (Benson, 2002). Some educators argue that only those countries where the student’s first language is the language of instruction are likely to achieve the goals of education for All. (Benson and Kosonen, 2013). Under the 6-3-3-4 system of education, teaching and learning of local languages have become mandatory (Uti and Iloh, 1989).Translation of study books, device manuals, newspapers, journals, etc. has always posed barriers to learning. Some of the barriers translation might pose to learners include the fact that translation teaches learners about languages, but not how to use it; it does not help learners develop their communication skills. (Duff, 1990; Deller and Rinvolucri, 2002) Some advanced countries such as United States of America maintain useful online corpuses through support of their government agencies to help reduce translation problems. As at the time of this study, Nigeria has not achieved such laudable feat.
Motivation of the Study
This paper was motivated by the strong desire and recommendation of the policy that established the Universal Basic Education (UBE), that is, that the pupils’ native language should be the language of preparation and delivery of learning experiences to the pupils. The National Commission of Colleges of Education (NCCE) categorically declared her preference and strong support for the use of native language in teaching pupils in nursery and primary stages of education in Nigeria. (Emenanjor, 2004). The huge successes recorded in pupils performances in some foreign countries, particularly in Asia countries of Japan and China, where comparatively higher performances have been proven to be due to the use of native language in their educational system, were added motivational factors. (Adjarho, 2014).
The difficulties in human translation of natural languages (Anya 2012; Ehiwuogu, 2008); efforts so far in Artificial Intelligence (“Artificial Intelligence”, 2008; Barker, et al, 2000); achievements in Natural Language Processing (Black et. al, 2000); the works of Ukwuani language development committee (Uti and Iloh, 1989) and Computer-Assisted-Instruction (Hontonyan et al, 2008) have created the feasibility assurance for this paper. Serious efforts must be made to bridge up the seemingly wide educational divide due to language of instruction in the early stages of the learners in Nigeria.
The Concept of Information and Communication Technology (ICT): Information refers to data that has particular meaning within a specific context. It is output of a processing activity. Communication refers to the transmission of information from one point to another. On the other hand, Technology is the application of science to accomplish desired objectives. The Concept of Information and Communication Technology (ICT), therefore, is a computer-based technology used to process, manage, store and transmit data.
Kinds of Information and Communication Technologies: Okeh and Opone (2010) vividly discussed some ICT technologies as follows:
Sensing Technology: These are ICT devices that will help in gathering information from the environment and transfer such information into a form that can be understood by the computer. Examples include keyboard, mouse, touch screen, etc.
Communication Technology: These are technologies that tie together and communicate information between the various kinds of technologies. Examples include land and cellular telephones, computer network, telecommunication network, television, radio, etc.
Analyzing Technologies: The computer hardware and software come within this category. Computer accepts data from sensing and communication devices and then store or process the information. These may include small, medium, and large computers.
Display Technologies: These technologies are essentially output devices. They make processed data available to human for use, either through sight or sound. Examples include display screens, printers, audio output devices such as loud speakers, etc.
Storage Technologies: These help to store large quantities of information in a form that can be easily accessed. This is made up of secondary memory of the computer known as secondary storage devices such as magnetic tapes, magnetic disc, read only memory (ROM),Video Compact Disc (VCD),etc.
The Concept of Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is a form of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that extracts meaning from human language to make decisions based on the information. This technology is still evolving, but there are already many incredible ways natural language processing is being used today. It is a technology used to aid computer understand the human’s natural language. It’s not an easy task teaching machine to understand how we communicate.
By “natural language” we refer to a language used for daily communication by human beings; languages like English, Hindi, Ika, Ukwuani or Portuguese. Natural Language contrasts to artificial languages such as programming languages and mathematical notations and it has evolved from generation to generation. It is not an easy task to pin down with explicit rules. The way we, humans, communicate with each other is Natural Language. Think about how much text you see each day: Signs, Menus, Email, SMS, Web Pages and the list is endless. Automated manipulation of natural language, like speech and text, by software is Natural Language Processing (NLP). It helps machines learn to communicate with each other and with humans in a meaningful way. Several decades of research resulted in development of NLP, however, the current word2vec technology has brought in path breaking results. In medicine, SNOMED-CT aids the development of NLP by use of indices and their relationships. Classification of digital documents in a uniform fashion is made easy and possible by this method.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) and computational linguistics so that computers and humans can talk seamlessly. NLP endeavors to bridge the divide between machines and people by enabling a computer to analyze what a user said (input speech recognition) and process what the user meant. This task has proven quite complex.
To converse with humans, a program must understand syntax (grammar), semantics (word meaning), morphology (tense), pragmatics (conversation). The number of rules to track can seem overwhelming and explains why earlier attempts at NLP initially led to disappointing results.
Adjarhor, (2014) states that natural language processing is posed with the challenges of representing grammar, syntax, semantic, morphology, synonymy, thesaurus, phonemes, idioms, phrases, clauses, speeches, lexicons or dictionaries and solving problems of ambiguity with computational models.
Technologies Based On NLP: Technologies constructed on NLP are becoming increasingly wide spread. For example, our phones that has the feature of predictive text and handwriting recognition; web search engines retrieves information locked up in unstructured text; machine translation reads and understands texts written in Chinese and re-read them in Spanish; text analysis assists us to detect sentiment in tweets and blogs. By providing a bridge between human and machine, accessing stored information, natural language processing plays a vital role in the multilingual society.
Categories of NLP: Modules of the natural language processing include: speech-to-text, text-to-text and text-to-speech. With the above three, the Speech-to-Speech Natural language processing system can be achieved. This shows that with the natural language processing systems, computers can read text, hear speeches, interpret it, measure sentiments and determine which parts are important.
Natural Language Processing Standard Architecture
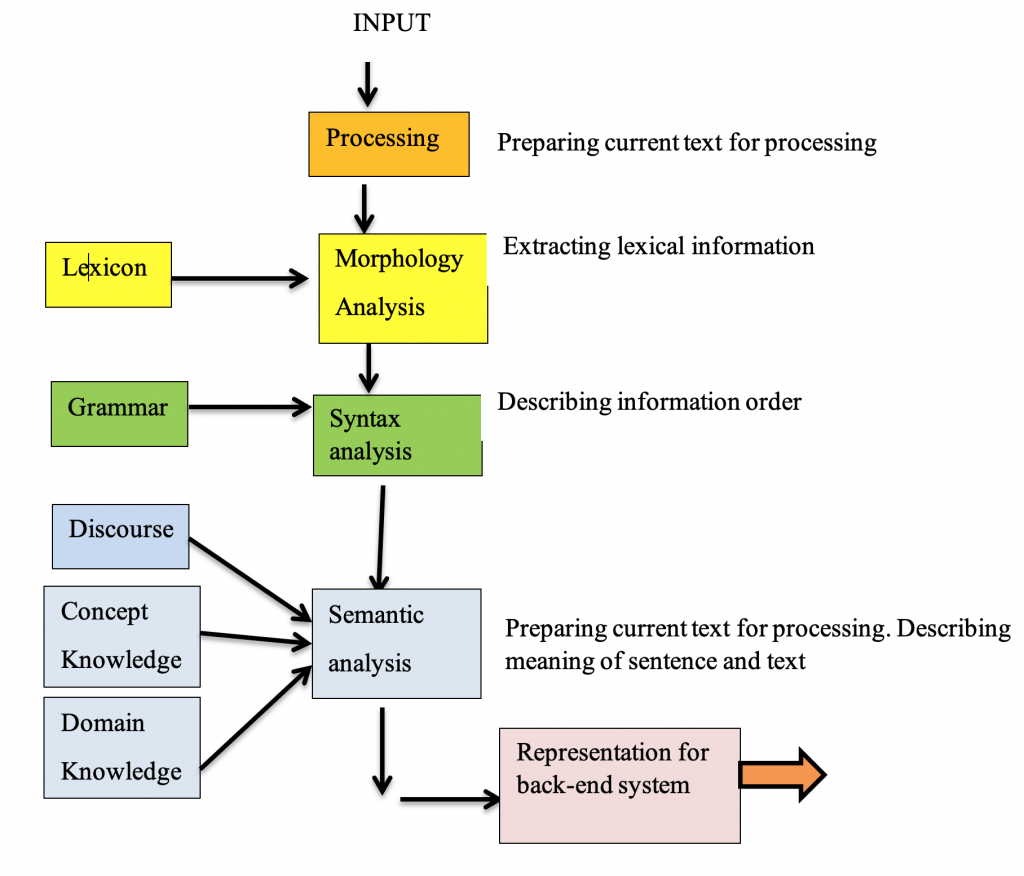
Problems Associated with Natural Language Processing:
The following problems are identified in this study.
- Computers will take a huge lot of time to carry out a perfect natural language processing.
- The general challenges possed by the various information and communication technologies which include failures of different forms can equally stand against natural language processing.
- The variability of natural languages makes natural language processing a difficult task to execute.
- A total adherence to the use of native language in teaching pupils in nursery and primary levels is not presently carried out in all places. Some teachers cannot speak neither do they understand the pupils native language. Above all pupils in are not taught with their native language.
- Machine translation facilities that can be used to develop speech-to-speech learning experiences in Nigerian native languages are not presently in existence.
- Some teachers in the Nursery and Primary levels of education in Nigeria cannot speak nor understand their pupils’ native language. This means they will always use the foreign English Language to prepare and deliver all learning experiences to the detriment of the pupils. They cannot also reinforce salient facts of learning experiences with pupils’ native language.
- Pupils of the nursery and primary education age in Nigeria are not proficient in reading or writing text materials yet the speech-to-speech module of natural language processing is not easy to achieve.
Speech Translation System: An Aspect of NLP: This is the process by which conversational spoken phrases are instantly translated and spoken aloud in a second language. This differs from phrase translation, which is where the system only translates a fixed and finite set of phrases that have been manually entered into the system. Speech translation technology enables speakers of different languages to communicate. It, thus, is tremendous value for human kind in terms of science, cross-cultural exchange and global business (https:// en.m.wikipedia.org/…/speech.).
Problems of Speech Translation System: Apart from the problems involve in the text translation, it also has to deal with special problems that occur in speech-to-speech translation, incorporating incoherence of spoken language, fewer grammar constraint of spoken language, unclear word boundary of spoken language, the correction of speech recognition, errors and multiple optional inputs.
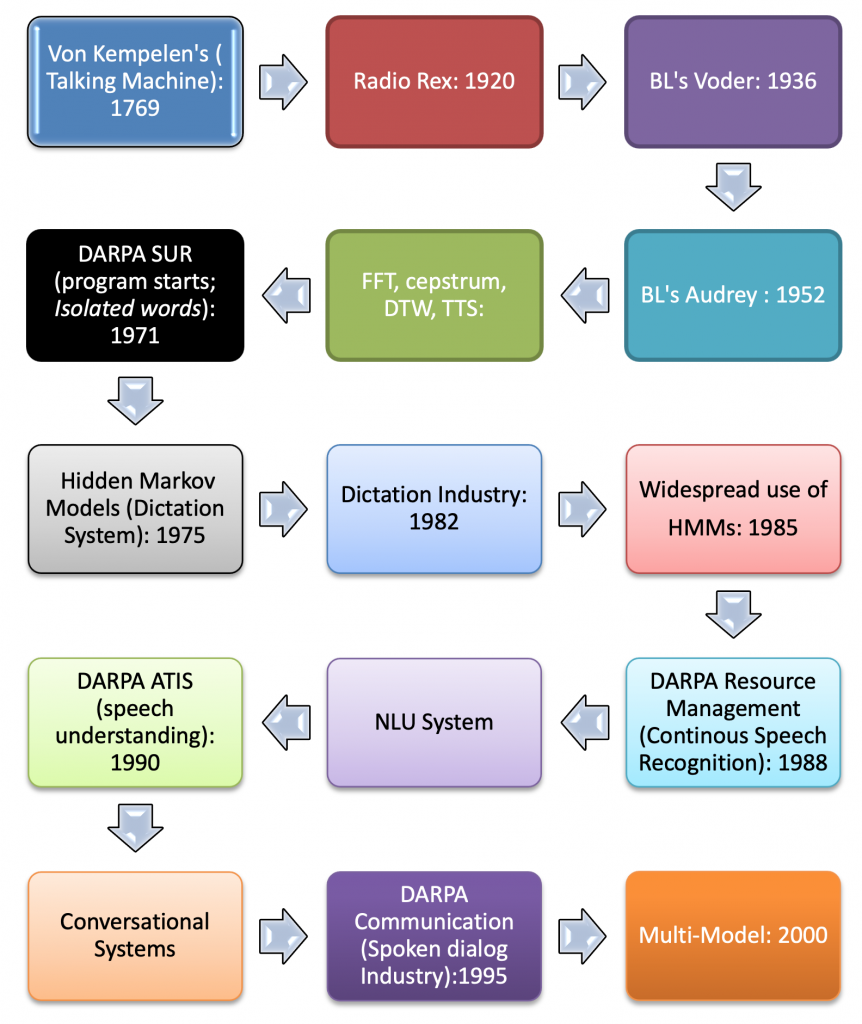
Spoken Language Technology Historical Account: Spoken language technology started long ago. In 1791, Wolfgan von Kempelen constructed and demonstrated a more elaborate machine for generating connected utterances. Apparently, Von Kempelen’s efforts antedate Kratzenstein’s since Von Kempelen purportedly began work on his device in 1769. It used a bellows to supply air to a need which, in turn, excited a single, hand-varied resonator for producing voiced sounds (Flanagan et al, 1965).
In 1920s, a commercial toy named Radio Rex was developed. However, Radio Rex has its lapses as it was regarded as crudest possible voice recognition. It was discovered that Radio Rex will not be able to respond to women or children since the technology of 500Hz vowel sound spectrogram was used. (David and Selfridge, 1962).
In 1769, Wolfgan became popular with his work on a fraudulent chess- playing Turn automation. Late in 1791 he came up with speech synthesizer. Following what is called “vox human” Christian Gottlieb was able to demonstrate the artificial vowel sounds of letters a, e, i, o, u, dictating their differences.
Kempelen classifies the vowels according to the width of the lip channel giving a ranking of A>E>I>O>U and the width of the so called tongue position. He goes on to remark that although he tried to produce the different vowels at the same pitch the vowel with a smaller tongue channel seem to be higher in pitch. It is a mechanical machine (Wolfgan, 2006).
Radio Rex: The first machine that recognized speech was probably a commercial toy named “Radio Rex” which was sold in the 1920’s. Rex was a celluloid dog than moved (by means of a spring) when the spring was released by 500Hz acoustic energy. Since 5ooHz is roughly the first format of the vowel (eh) in “Rex”, the dog seemed to come when he was called (David and Selfridge, 1962). The challenge of Radio Rex is the differences that exist between pronunciations of adult-male, adult-female, young-male and young-girl of course the toy dog mechanism described here is nowhere near automatic speech recognition that we are used to see nowadays, it goes not recognizes specifically anyone’s voice or converts speech to text that can be processed, but rather simply reacts to a frequently interval regardless of the person who can produce it (BL’s Voder, 1936).
DARPA SUR: Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) established the Speech Understanding Research (SUR) program to develop a computer system that could carry out speech conversion (https://books.google.com.ng/books.).
The achievements of Hidden Markov Models (Dictation System developed in 1975) gave worthy of note to the development of spoken language technology. Below are some examples of spoken language trends.
Illustration of Trends of Spoken Language Technology
Tools Useful in Natural Language Processing: For any Natural Language Translation System to be developed, maintained and used for efficient and effective result, appropriate devices and technologies must be brought into their rightful positions.
ICT is an umbrella term that includes any communication device, encompassing radio, television, cell phones, computer and network hardware, satellite systems and so on, as well as the various services and appliances with them such as video conferencing and distance learning. Others include applications and system software such as operating systems; web-based information and applications such as distance learning; telephones and other telecommunications products; video equipment and multimedia products that may be distributed on videotapes, CDs, DVDs, email, or the World Wide Web; office products etc. A few prominent examples include Email filters, Smart assistants, Search results, Predictive text, Language translation, Digital phone calls, Data analysis, and Text analytics. Computer is capable of exhibiting many patterns of human senses and as such has the capability of presenting information in varied forms with varied devices.
There are similarities between natural language processing and computer language processing particularly when the phases of compilation of high-level computer languages and phases of natural language translation are compared. The computer language processing and natural language processing involve Lexical Analysis, Syntax Analysis and Semantic Analysis. The major difference is that no single type of grammar has been found sufficient to generate an entire Natural Language. Moreover, Lexicons or dictionary or corpora are not used as tools in computer language processing. Computer language has finite list of reserved words and infinite list of user-defined words. On the other hand, natural language word belong to classes called part of speech and words increase in number from time to time and some are even borrowed from other native languages.
Lexical Analysis − It involves identifying and analyzing the structure of words.
Syntactic Analysis (Parsing) − It involves analysis of words in the sentence for grammar and arranging words in a manner that shows the relationship among the words, to explain but just two out of the numerous components. It is evidently clear that without ICT there can be no NLP.
The role of NLP in Bridging Educational Divide: Natural language processing helps computer communicate with humans in their own language and scales other language-related tasks. For example, NLP makes it possible for computers to read text, hear speech, interpret it, measure sentiment and determine which parts are important. It is therefore useful presenting learning materials at grassroots level to the early learners. Those who dread foreign language can through NLP find themselves at home in their search for knowledge.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has entered the mainstream and integrates with Big Data. Take the business traveler. Today, when he or she stays at a hotel, like Wynn Las Vegas, the customer can bypass the front desk when getting extra towels or ordering room service. Thanks to Amazon’s Echo and its use of NLP, a hotel concierge may no longer be necessary. In this new world, Big Data flows in the form of speech, a loop between hotel guest and computer. All the guests have access to this technology. Wynn Las Vegas has already added Amazon Echo devices to each of its 4,748 hotel rooms. As consumers become more familiar with NLP and its time savings benefits, they will be more likely to adopt Natural Language Processing in the home and office, for other tasks. NLP will change everything, from Business Reporting and Data Analytics/Synthesis to Security and Data Governance. The future has arrived.
Question answering technology built on 200 million text pages, encyclopedias, dictionaries, thesauri, taxonomies, ontologies, and other databases has gained traction. AI has helped data-rich companies such as America’s West-Coast tech giants organize much of the world’s information into interactive databases such as Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Additionally, speech-to-speech translation also has its advantages compared with text translation, including less complex structure of spoken language and less vocabulary in spoken language.
1- Mental Illness Analysis: Measure how countless linguistic features of conversations are connected with conversation outcomes. By applying models that are associated with better conversation outcomes as sequence-based conversation models, language model comparisons, message clustering, and psycholinguistics-inspired word frequency analyses, to discover actionable conversation strategies.
2- Mining Electronic Health Records for Mammography Research — associating mammographic and pathologic results in clinical decision support using natural language processing and data mining methods.
3- NLP Algorithm and Asthma Ascertainment — Application of a Natural Language Processing Algorithm to Asthma Ascertainment through an Automated Chart Review
4 – Natural Language Processing for On-Site Search: If you have or use an e-commerce site, you must be very familiar with natural language processing (NLP) being used in Site Search. More than just another path, NLP has been identified as a powerhouse in the realm of on-site search and has brought in vast number of advantages packaged up only for those who focus on improving their business by improvising their site search capabilities.
Even though the development stage is little complex, using NLP in the applications has lots of advantages which also include:
Automatic Summarization: It produces a readable summary of a part of the text.
Coreference Resolution: It determines which words refer to the same objects, out of the given sentence or larger portion of text.
Discourse Analysis: This includes several related tasks such as identifying the discourse structure of connected text.
Better Results All the Way Around: It is beyond keyword matching or text-oriented search; meaning-to-meaning search provides results that are correct according to the form of the input text, whereas NLP delivers applicable results as soon as your customer hits “search.” Understanding the intension of the customer.
Search Processing Translates the Intention of Your Customer: Your customers are human beings, which means they’re not 100 percent accurate in communication. They make spell errors; they may confuse brands with products and forget product or service details — It depends on how robust your on-site search is to fill the gap when these errors happen. NLP connects the dots to keep search unified, even in the scenarios like typos or abrupt information.
More Data Extracted Means More Data for Growth: Measuring what your customers intend to search is key in improving your business. Through NLP, you can learn about customer habits, preferences, and tendencies across your entire consumer base. This data can be re-applied across several phases of your business, from marketing to SEO, doing campaigns to sales and promotions and a lot more.
Complex Search Options Affects Results: The ability to handle numerous variables in a single search means providing a collective result that’s suggestive of your customer’s end needs. Natural language processing looks at a broader picture, not just the user input keywords in a search, providing results that are the summation of their parts. Results that might be wrongly recognized by text-based searches or accidentally misplaced or missed out from keyword queries.
Contextual Understanding Delivers Answers: Today’s search engines are confining to Q&A boxes — customers ask questions and expect answers. In addition to the complicated search options afforded by NLP, your customers can raise questions freely and get to products they’re looking for. Question based searches calls out a huge challenge in your skill-set to serve customers who might not be using the technical keywords or main phrases in their search for a specific product.
The above variables embedded in your search website contribute to fast hit of your e-commerce websites looking for to better serve their customers — and they can all be credited to natural language processing, which is as simple as human language!
Su (2015) presented some objectives of his Speech-To-Text systems to include the human computer interface developed to communicate or interact conveniently for one who is suffering from some kind of disabilities. Speech–To–Text (STT) systems have a lot of benefits for the deaf or dumb people and find their applications in our daily lives. The aim of his system is to convert the input speech signals into the text output for the deaf or dumb students in the educational fields..
Summary: For an effective implementation of Natural Language Processing, very many useful tools and technologies will be involved. These fall under the general name called ICT. It is evidently clear that without ICT there can be no NLP.
Conclusion: Natural Language Processing (NLP) combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) and computational linguistics so that computers and humans can talk seamlessly. For any Natural Language Translation System to be developed, maintained and used for efficient and effective result, appropriate devices and technologies must be brought into their rightful positions. Natural language processing is posed with the challenges of representing grammar, syntax, semantic, morphology, synonymy, thesaurus, phonemes, idioms, phrases, clauses, speeches, lexicons or dictionaries and solving problems of ambiguity with computational models.
References:
“Artificial Intelligence”, (2008) Microsoft Encarta (R) 2009. (DVD). Redmond, WA: Microsoft Corporation.
Adjarho, D.O (2014) Towards Developing a Language Translator for Primary Education in Nigeria. A Ph.D Thesis, University of Benin, Benin City.
Anya, C., (2012). Essentials of Ika Grammar, Nick Prints Associates, ISBN:978-49546-1-5.
Barker, K and Cornacchia, N. (2000). Using Noun Phrase Head To Extract Document Key Phrases In: Hamilton H.J. (Ed) Advances In Artificial Intelligence. Proceedings Of 13thBiennial Conference Of The Canadian Society Of Computational Studies Of Intelligence, AI 2000, 14-17 May 2000, Montreal, Berlin: Springer –Verlag Pp 40-52.
Benson, C. and Kosonen, K. (2013). Language Issues in Comparative Education: Inclusive Teaching and Learning in Non-dominant Languages and Cultures. Rotterdam: Sense Publishers.
David, E.E and Selfridge, O.G (1962) Bell Telephone Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers, May 1962, Volume 50 Issues:5 PP 1093-1101, ISSN 0096-8390. Distal Object Identifier.
Deller, S. and Rinvolucri, M. (2002). Using the Mother Tongue: Making the Most of the Learner’s Language, Delta Publishing Company.
Duff, A. (1990). Bringing Translation back into the Language Class. Practical English Teaching 10/3.
Ehiwuogu, F.O (2008). Gwan Gwai: A Reference book for learners of Ika Language, Ukor Press 20 Iregwa Street Agbor.
Emenanjo, E.N. (2004). Ultilingualism Miniority Languages and Language Polcy in Nigeria. Central Book Limited, Plot 1, Ewuru Industrial Estate, Agbor, in Collaboration with the Linguistic Association of Nigeria.
Flanagan, J.L. and Selfridge, O. G. (1965). Speech Analysis, Synthesis and Perception. Springer-Verlage, PP 166-167.
Hontonyan, A.B, Dalmeida, I and Edum, T.A (2008), Utilizing Computer Assisted Instruction (CAI) in Teaching and Learning of Agricultural Science. Akoka Journal of Pure and Applied Science Education (AJOPASA). Vol 10 No 1, ISSN: 11187070, July 2008, 101-108.
Kosonen, K. (2005). Education in Local Languages. Policy Practice in Southeast Asia. First Language First: Community-Based Literacy Programmes for Minority Language Context in Asia. Bangkok: UNESCO Bangkok.
MichelleKnightJuly 13, 2017): NLP: The What, Why, and How.
SU, M.M. (2015). Speech-To-Text (STT) Conversion System using Hidden Markov Model (HMM). International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research. Volume 4, Issue 06, June 2015. ISSN 2277-8616.
UNESCO (1953). The Use of the Vernacular Languages in Education. Monogragh on Foundations of Education, No 8. Paris: UNESCO.
UNESCO (2008). Other Tongue Instruction in Early Childhood Education: A Selected bibliography. Paris: UNESCO.
Uti, J.O. and Iloh, F.N. (1989) . Introduction to Ukwuani Orthography, Numerals, Measurements and Time. Benin-City, Ambik Press.
Wolfgan V.K (2006). History of Computers and Computing www.w3.0rg/ https://books.google.com.ng/books.
